Sections
If you would like to transfer your domain to another provider, whilst keeping your existing data, ie. website(s), database(s) and Emails, you are able to first test the website, followed by pointing the domain to the new provider, to test their environment, prior to actually transferring the domain across.
You should never transfer a domain prior to taking a backup of your data and then uploading the data to the new server.
Let’s look at the below options closely to enable testing and correct pointing, ensuring that all services remain active during this process.
TESTING
EDIT WINDOWS HOSTS FILE
By editing the hosts file, you “fool” your browser into thinking that you are visiting the actual website, which will display correctly. The first question you should ask, is how would you know you are viewing the correct site, seeing that the current site is still live on your existing provider’s servers?
This can be done by viewing the SSL status of the website. Is the padlock reflecting in front of the website link or not? If your current site is secure then you can identify the test site by the non-secure status. Another way is to add a character to
- Hit the Windows key.
- Type Notepad in the search field.
- In the search results, right-click Notepad and select Run as administrator.
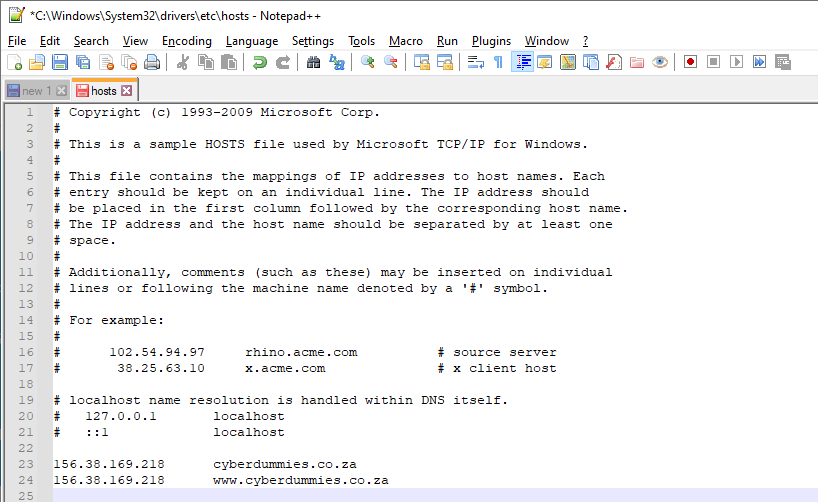
- From Notepad, open the following file: c:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc\hosts.
- Make the required changes to the file (Add the IP address of the new server followed by the domain name, which is your website address).
- Select File > Save
Below view of IP address of new server, enabling you to view the website.
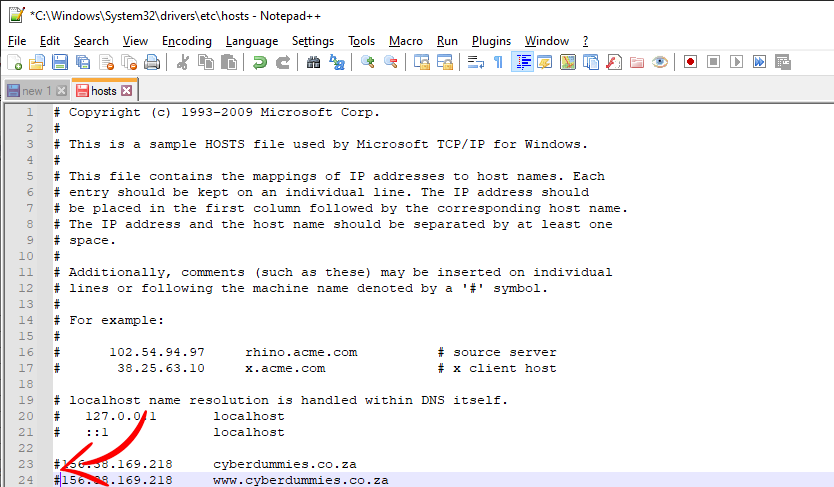
Notice the “#” below in front of the IP if you want to block the site on the new server and perhaps view the existing site with your current provider.
DOMAIN POINTING
UPDATE THE DNS (Website and Mail) RECORDS ONLY
What is DNS?
DNS or Domain Name System translates domain names into IP addresses.
If you are completely satisfied with the website, you can update the DNS records for the site. In order to do this you have to access the host panel of your current provider.
The details would have been sent to you by your current provider, or you can request these from them.
- Before updating the website records, make sure that the website files and database(s) have been restored on the new server
- Once logged into the host panel, you will be able to edit the following records
– A / www records (these are the website records and should display the server IP of your new host, eg. 123.456.789.100 - The below records should NOT be altered in any way, to ensure your mail service is not interrupted
– MX records (aka Mail Exchange, reflecting the hostname for the mail server, ie. mx.hostname.co.za
– There are other MAIL records you should also leave, such as “mail”, “pop3”, “imap”, “smtp” - When only updating the DNS, the name servers will continue to reflect the host name of your existing provider.
CHANGE THE NAME SERVERS
What is a name server?
A name server helps to translate IP addresses into domain names.
Now that you have viewed your website and completely satisfied, you can update the name servers. ALL services will now run via the new provider.
There are certain steps to take before you go ahead and update the name servers in the client / billing area.
- Email accounts have to be created on your hosting space with the new provider and existing Emails should be migrated (moved) across to the new server.
– Your new provider can advise or even assist with this process - Ensure that you have taken a backup of the data (website, database, Emails) in case this is required by the new provider
- Only update the name servers if you are completely satisfied with the services of the new provider. This way you will be able to change the DNS records back to reflect the details of your current provider, before committing to the transfer.
Keywords:
point a domain, point domain, domain pointing, dns pointing